Product Description
Graphite insulation felt is based on polyacrylonitrile-based carbon felt or graphite felt. It is formed after a special combination of curing, shaping, carbonization, and high-temperature treatment. It has good shape retention, self-supporting, and has a small specific gravity. Fiber shedding, high surface finish, low thermal conductivity, high-temperature resistance, good thermal shock resistance (no cracking or deformation after long-term use), long service life, easy installation, and replacement, and the operating temperature can reach 3000 ° C. It is a high-temperature vacuum equipment, A new thermal insulation material ideal for high-temperature equipment in a non-oxidizing atmosphere. It is suitable for various furnace types such as vacuum high-pressure gas quenching furnaces, vacuum sintering furnaces, pressurized vacuum sintering furnaces, monocrystalline silicon furnaces, polycrystalline silicon furnaces, and silicon carbide recrystallization furnaces.
Product Classification
Ragid Graphite Felt
Cured graphite felt is also called rigid felt. According to the different fiber lengths in the hard felt, it is divided into long fiber hard felt and short fiber hard felt. Long-fiber hard felt is a soft felt that is impregnated with resin and then laminated, solidified, and graphitized to form a graphite felt with a certain shape and self-sustainability. Short fiber hard felt is made by breaking the carbon fiber into pieces, adding a binder, then shaping, solidifying, and graphitizing. The density of hard felt is generally higher than that of soft felt. In addition, various forms of surface treatment can be carried out, such as graphite paper, carbon cloth, charcoal/charcoal and coating, etc. At the same time, according to the different types of carbon fiber raw materials, hard felt can be divided into asphalt-based hard felt, polyacrylonitrile-based hard felt, viscose-based hard felt, etc.
| Material |
Density |
Ash content (PPM) |
Compresive Strength (Mpa) |
Bending Strength |
Thermal Conductivity (W/mK) |
Thermal Expansion Coefficient (x10-6/°C) |
||||
| 500 | 20 | 5 | Face Direction | Lateral Direction | Face Direction | Lateral Direction | 1500°C (vacuum) | 1000°C | ||
| Asphit Base (Long Fiber) |
0.13 | Yes | Yes | Yes | 0.35 | 0.10 | 1.45 | 0.70 | 0.28 | 2.20 |
| 0.16 | Yes | Yes | Yes | 0.45 | 0.12 | 1.60 | 1.00 | 0.25 | 2.20 | |
|
Viscose Base |
0.16 | Yes | Yes | 0.52 | 0.25 | 2.21 | 1.25 | 0.40 | 2.50 | |
|
Viscose Base |
0.17 | Yes | Yes | 0.40 | 0.25 | 2.00 | 1.10 | 0.40 | 2.45 | |
| PAN Base (Short Fiber) |
0.16 | Yes | Yes | 0.60 | 0.25 | 2.50 | 1.45 | 0.50 | 2.50 | |
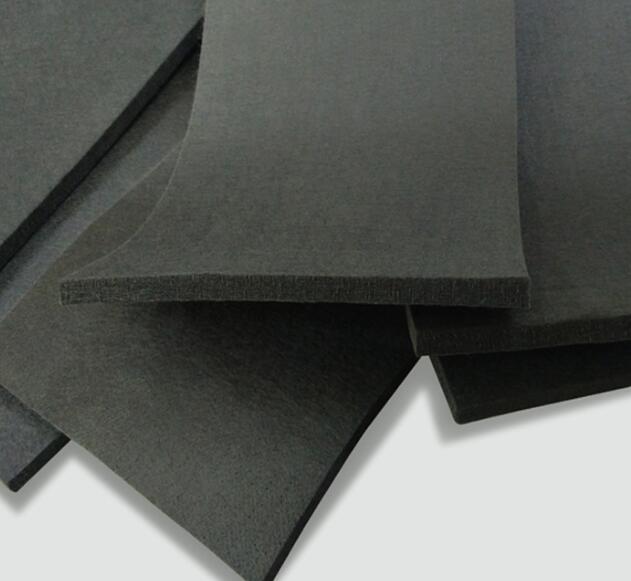


Soft Graphite Felt
Viscose graphite felt also called soft graphite felt is made of viscose fiber as the base material, which is formed after high-temperature treatment of pre-oxidation, carbonization, and graphitization. It has good shape retention, self-supporting, small specific gravity, no short fiber shedding, high surface finish, low thermal conductivity, high-temperature resistance, good thermal shock resistance (long-term use without cracking, no deformation), long service life, is easy to install and disassemble, and the operating temperature can reach 3000 ℃. It is an ideal new thermal insulation material for high-temperature vacuum equipment and high-temperature equipment in a non-oxidizing atmosphere.
| Model | Thckness (mm) |
Density (g/cm3) |
Width (mm) |
Ash Content (PPM) |
Carbon Content (%) |
Sulfur Content (PPM) |
Thermal Conductivity (W/mK) |
Tensile Strength (Mpa) |
| HT-SVG01 | 5, 10 | 0.08-0.11 | 1200, 1350 | ≤500 | >99.95 | ≤200 | 0.20-0.22 | 0.10-0.14 |
| HT-SVG02 | 5, 10 | 0.08-0.11 | 1200, 1350 | ≤200 | >99.98 | ≤30 | 0.23-0.26 | 0.10-0.14 |
| HT-SVG03 | 5, 10 | 0.08-0.11 | 1200, 1350 | ≤20 | >99.99 | ≤5 | 0.24-0.28 | 0.10-0.14 |
| HT-SVG04 | 5, 10 | 0.10-0.13 | 1200, 1350 | ≤20 | >99.99 | ≤5 | 0.24-0.28 | 0.18-0.25 |
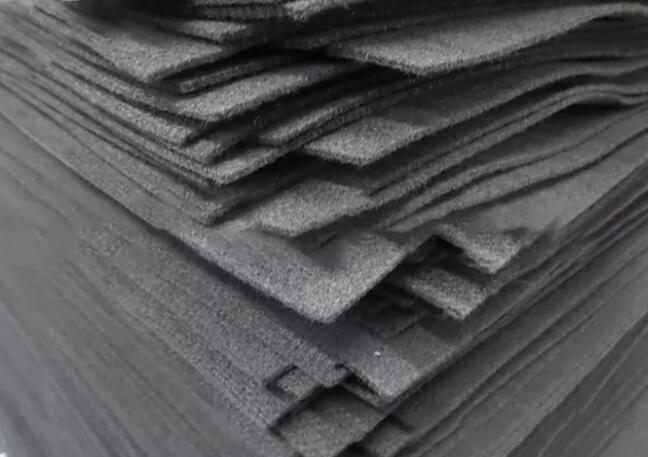


Product Application
Packing Photos


Click directly to send a message via WhatsApp
can not be empty
The E-mail format is not correct
can not be empty
can not be empty
